UPPER DOAB SUGAR MILLS

Arial View of Upper Doab Sugar Mills
Sir Shadi Lal Enterprises Limited started its business in the year 1933 with a Sugar Factory called Upper Doab Sugar Mills with a cane crushing capacity of 600 TCD per day at Shamli, Distt. Muzaffarnagar (U.P.). Shamli is about 40 kms. from Distt. Muzaffarnagar (UP), about 70 Kms. from Distt. Saharanpur (UP) and about 100 kms. from Delhi. The Company has been constantly modernizing its plant & machinery in stages by adopting the latest technology and presently working with a cane crushing capacity of 7500 TCD per day.
The major expansion projects taken up by the Company at various stages for the Sugar Mill at Shamli are summarized below:-
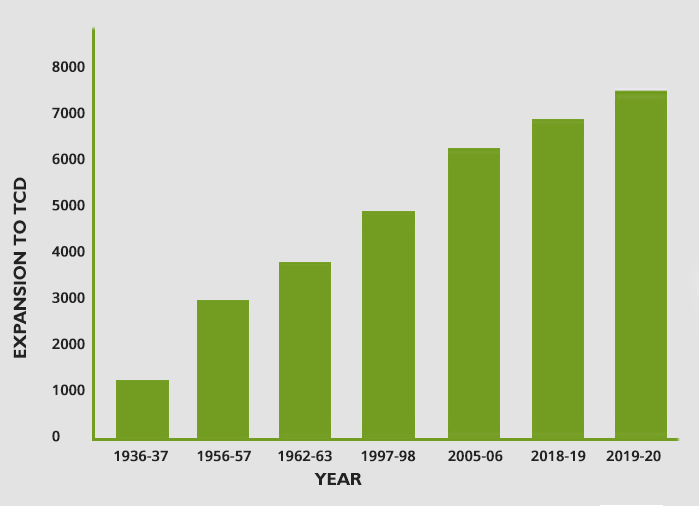
| Year | Expansion to (TCD) |
|---|---|
| 1936-37 | 1200 |
| 1956-57 | 3000 |
| 1962-63 | 3810 |
| 1997-98 | 5000 |
| 2005-06 | 6250 |
| 2018-19 | 7000 |
| 2019-20 | 7500 |
As a result of constant modernization and expansion, the crushing capacity
of the Sugar Mill Plant at Shamli has increased to the present level of 7500
TCD per day. The capacity utilization of the Plant for the last number of
years has been maximum. Being a seasonal industry, the Sugar Factory works
for about 180-210 days in a year.
The manufacturing results of our sugar unit for the last three crushing seasons are detailed below :
| SUGAR SEASONS (Upper Doab Sugar Mills) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-18 | 2016-17 | 2015-16 | |
| Gross Working Days | 214 | 198 | 162 |
| Total Cane Crushed(Qtls) | 11563000 | 10273029 | 8096851 |
| Average Cane Crushed per Crop day (Qtls) | 54033 | 51884 | 49981 |
| Manufacturing losses (%) | 1.98 | 1.95 | 1.9 |
| Sugar Recovery (%) | 10.87 | 10.46 | 10.11 |
| Total Sugar produced (Qtls.) | 1257930 | 1074380 | 822850 |
Intricacies Involved
Sugarcane is broadly classified into three varieties - early, general and unapproved. Cane is sowed during February and October every year. The first seed growth is known as the plant and subsequent growth after harvesting from the stem is known as Ratoon. The early variety has more sugar content than the general variety.

Cane Yard

Cart-Weightment Cabin
Every farmer within the command area of the Mill is provided with a calendar, which tells him when he can expect a Mill Supply Ticket (Purchy), against which he will deliver the sugarcane.
He then harvests the cane and transports it either in a bullock cart or tractor trolley to the mill. Cane is also bought at the mill's own centers within the command area. This cane is then transported in trucks or through rail to the mill.

Trolley Weightment Cabin

Truck Weightment Cabin
Harvested cane now can be transported through truck also to the mill. Cane is also bought at the mill's own centers within the command area. This cane is then transported in trucks or through rail to the mill.
The manufacturing of sugar begins when harvested cane is
received at the mill gate, after which cane is weighed
on the platform type weighbridges. This has the weight
recording arrangement linked to a computer that records
the gross and net weights as well as the price payable
to the farmers. Cart cane gets unloaded directly into
the cane carrier and tractor trolleys whereas truck cane
is unloaded with the help of overhead traveling cranes.
Cane is weighed using an electronic weighbridge and
unloaded into cane carriers. It is then prepared for
milling by knives and shredders. Sugarcane juice is then
extracted by pressing the prepared cane through mills.
Each mill consists of three rollers:
- Extracted juice mixed with water is weighed and sent to the boiling house for further processing. Residual bagasse is sent to boilers for use as fuel for steam generation
- This juice is heated and then treated with milk of lime and sulphur dioxide. The treated juice is then further heated and sent to clarifiers for continuous settling. The settled mud is filtered by vacuum filters and filtered juice is returned to be further processed while the oliver cake is sent out
- The clear juice is evaporated to a syrup stage, bleached by sulphur dioxide and then sent to vacuum pans for further concentration and sugar grain formation. Crystals are developed to a desired size and the crystallized mass is then dropped in the crystallizers to exhaust the mother liquor of its sugar as much as possible. This is then centrifuged for separating the crystals from molasses. The molasses is re-boiled for further crystallization.
Thus, the original syrup is desugarised progressively (normally three times) till finally, a viscous liquid is obtained from which sugar can no longer be recovered economically. This liquid, which is called final molasses, is sent to the distillery for making alcohol. The sugar thus is separated from molasses in the centrifuge is dried, bagged (50 Kg and 100 Kg), weighed and sent to storage houses.Sugar is made in different sizes and accordingly classified into various grades i.e. large, medium and small.
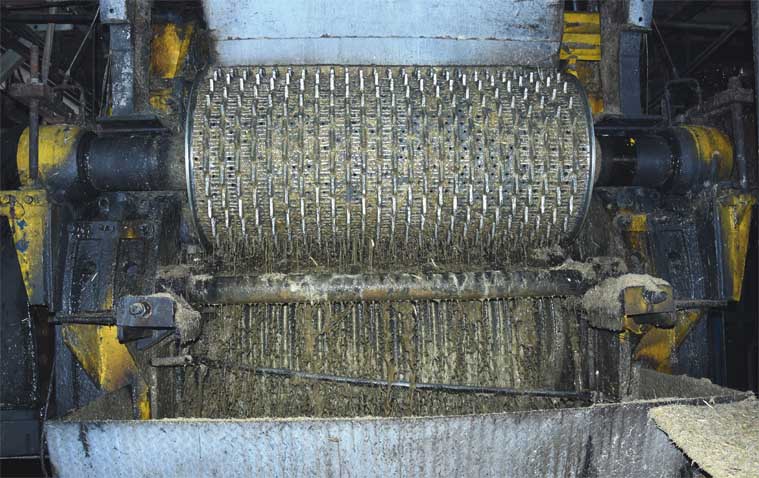

Cane Juce Machine

Sugar Process

Sugar Packging
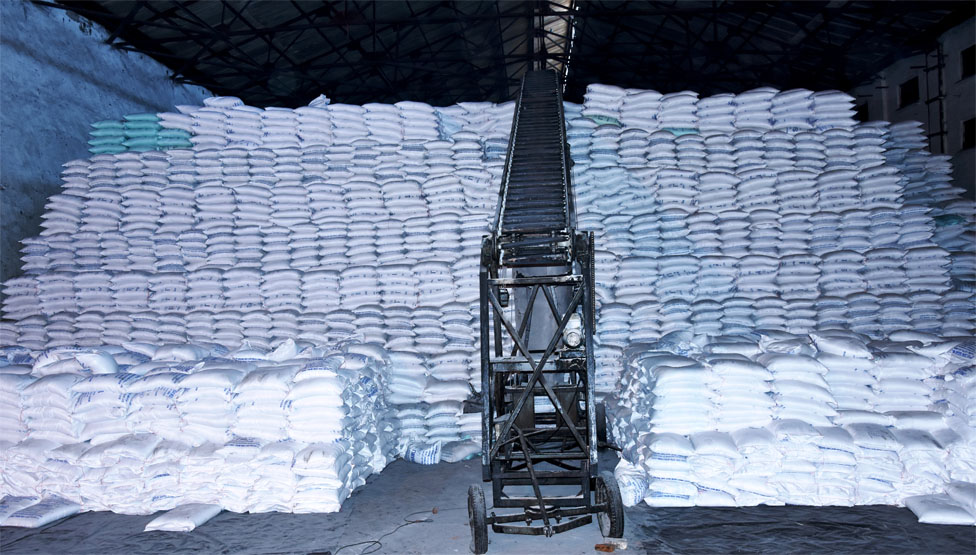

Sugar Storage

Sugar Bags
Molasses
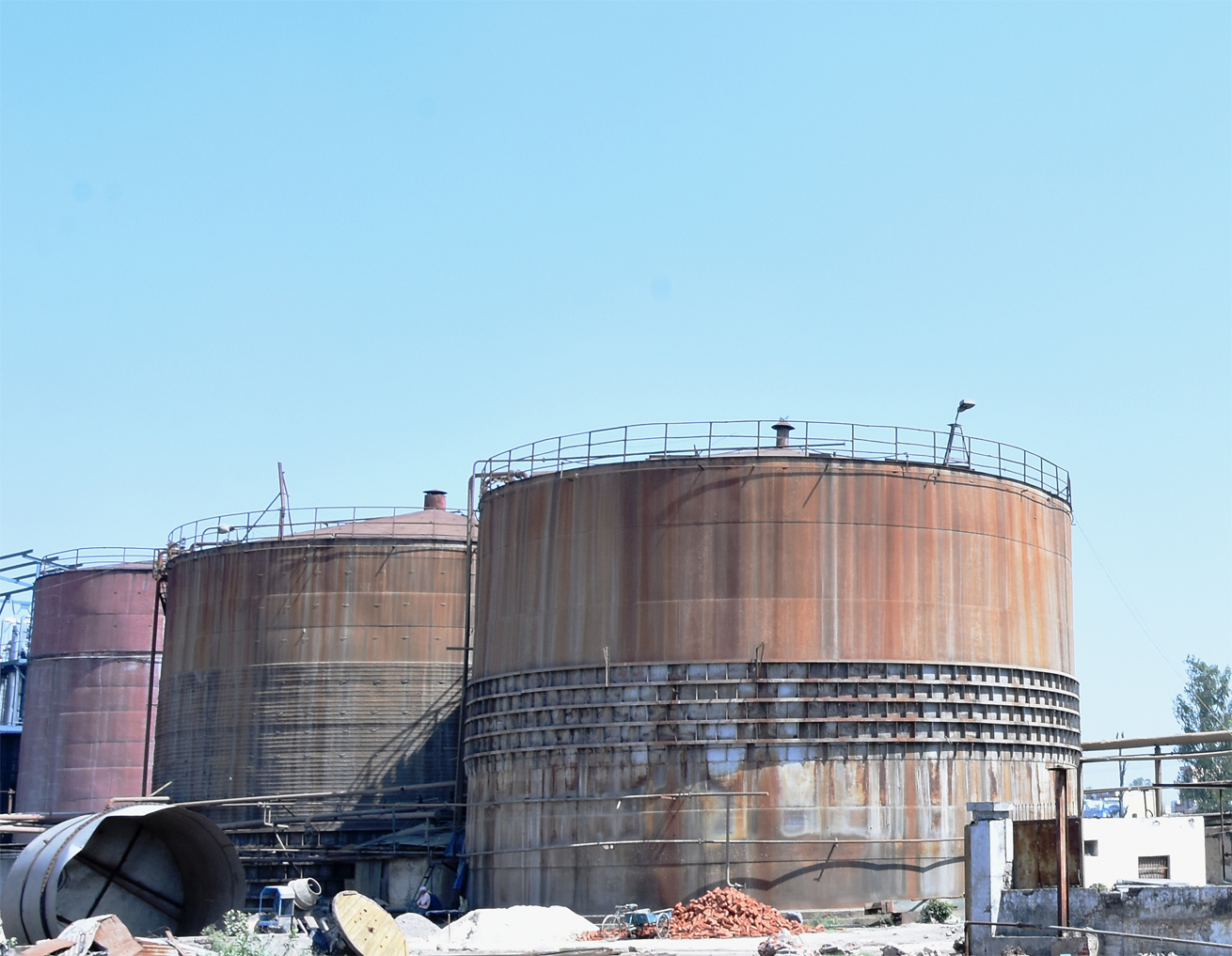

Molasses Storage Tank
Molasses is one of
by-product obtained in the preparation of sugar
through repeated crystallization. The yield of
molasses per ton of sugarcane varies in the
range of 4.5% to 5%. Molasses is mainly used for
the manufacture of alcohol, yeast and cattle
feed.
Alcohol in turn is used to produce ethanol,
rectified spirit, potable liquor and downstream
value added chemicals such as acetone, acetic
acid, butanol, acetic anhydride, MEG etc.
The state government controls the export of
molasses through export licenses issued every
quarter. Molasses and alcohol-based industries
were decontrolled in 1993 and are now being
controlled by respective state government
polices. Nearly the industrial alcohol
manufacturers consume 90% of molasses produced
and the remaining 10% is consumed by the potable
alcohol sector.
Bagasse

Bagasse Yard
Bagasse is a fibrous
residue of cane stalk that is obtained after
crushing and extraction of juice. It consists of
water, fibre and relatively small quantities of
soluble solids. The composition of bagasse
varies based on the variety of sugarcane,
maturity of cane, method of harvesting and the
efficiency of the sugar mill.
Bagasse is usually used as a combustible in
furnaces to produce steam, which in turn is used
to generate power. It is also used as a raw
material for production of paper and as
feedstock for cattle.
By making use of bagasse sugar mills have been
successful in reducing their dependence on the
State Electricity Boards, for their power supply
as it can procure up to 90-95% of its total
power requirement through captive generation
from steam turbines.
Press mud

Press Mud
Press mud, also known as oliver cake or press cake, is the residual output after the filtration of the juice. It is mixed with spent wash from the distillery and cultivated to produce high quality bio-manure.
Home
